Amorphous alloy for BRAZING FILLER METALS
Product Catalog Download
Click here to download the product catalog
Contact
Soft Magnetic Materials and Components (for Waxwood)
Feature

Amorphous brazing filler metal has the following characteristics.
- Toughness, flexibility, 100% metal
- Melts quickly over a narrow temperature range
- Strongly bonded with few voids
- Can be installed between joining parts with high precision
- Economical and efficient (compared to powder brazing filler metal)
- Assembly process can be reduced
- No contamination of the environment or brazing furnace
- Easy to punch and bend
Reducing the amount of brazing filler metal
Since it is in the form of a foil with a thickness of 25 to 40 μm,
the amount used can be reduced by approximately 50% compared to paste,
contributing to lower brazing material costs.
Comparison of usage reduction rate
(compared to our company)
| Filler metal | Filler thickness (μm) |
Net filler usage amount (g) |
Usage reduction rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BNi-15 paste | - | 3.308 | 100 |
| MBF67 foil | 38.1 | 2.309 | 30 |
| MBF67 foil | 25.4 | 1.560 | 53 |
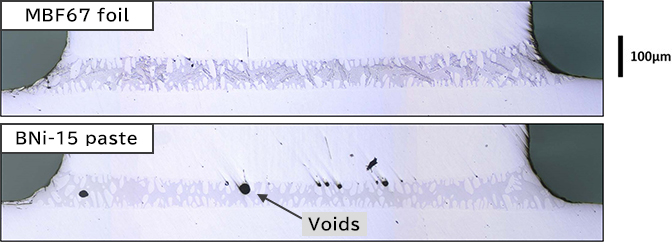
Fewer voids at brazed joint
Since solder foil does not contain a binder like paste material, there are almost no voids (cavities) formed in the bonding layer due to the binder removal process, resulting in a highly reliable bonded product.
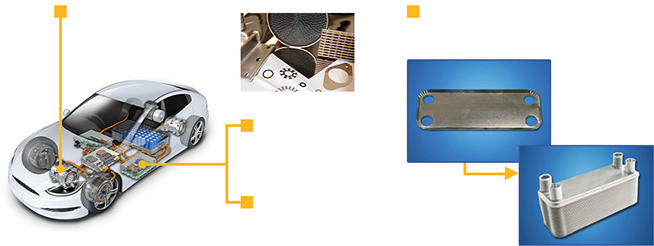
Application
EGR cooler
Plate-Heat exchanger
Metallic catalytic
substrate
Exhaust heat
recovery unit
Stamped
Brazing Foil
Product lineup
| MBF Alloy |
AWS & AMS Standard |
Nominal Composition (wt %) |
Temperature (℃) |
Brazing temperature (℃) |
Density x 103 (kg/m3) |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Fe | Si | C* | B | P | Mo | Ni | Solidus | Liquidus | ||||
| 15 | 13.0 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 0.03 | 2.8 | - | - | Bal | 965 | 1103 | 1135 | 7.82 | |
| 20 | AWS BNi-2 /AMS 4777 |
7.0 | 3.0 | 4.5 | 0.06 | 3.2 | - | - | Bal | 969 | 1024 | 1055 | 7.88 |
| 30 | AWS BNi-3 /AMS 4778 |
- | - | 4.5 | 0.06 | 3.2 | - | - | Bal | 984 | 1054 | 1085 | 8.07 |
| 50 | AWS BNi-5a |
19.0 | - | 7.3 | 0.08 | 1.5 | - | - | Bal | 1052 | 1144 | 1170 | 7.70 |
| 51 | AWS BNi-5b |
15.0 | - | 7.3 | 0.06 | 1.4 | - | - | Bal | 1030 | 1126 | 1195 | 7.73 |
| 60 | AWS BNi-6 |
- | - | - | 0.1 | - | 11.0 | - | Bal | 890 | 890 | 920 | 8.14 |
| 62 | 21.0 | <1 | 0.5 | - | 0.5* | 8.0 | 1.0 | Bal | 878 | 940 | 1020 | 7.74 | |
| 67 | 25.0 | <1 | 1.5 | - | 0.5* | 6.0 | 1.5 | Bal | 890 | 970 | 1020 | 7.70 | |
| 601 | 16.0 | 32 | 1.5 | - | 0.5* | 6.0 | 1.5 | Bal | 960 | 1030 | 1060 | 7.57 | |
| 80 | AWS BNi-9 |
15.0 | - | - | 0.06 | 4.0 | - | - | Bal | 1048 | 1091 | 1120 | 7.94 |
- *(Maximum concentration)
Online purchase

Standard thicknesses are 25.4 μm and 38.1 μm. Some alloys are also available in 50.8 μm and 76.2 μm sizes.
The maximum width is 215.9 mm.
30kg/lot. Please contact us for sample products.
It will take about 3 to 4 months after you place your order.
Please contact to Metglas™, Inc.
It has the same bonding strength as paste brazing filler metal.
Vacuum brazing or atmosphere brazing (nitrogen, inert gas, etc.).
Our series does not include brazing filler metals for ceramics bonding. Active filler metals are used for ceramics bonding.
Since it is made of metal foil, it can be stored for a long time (does not contain binders, etc.).
Copper brazing filler metals are used because of their high bonding strength and nickel alloy brazing filler metals are used because of their high heat resistance and high corrosion resistance.
It is possible.
In contrast to welding, which joins materials by melting the base materials, brazing joins materials without melting the base materials. Therefore, it is excellent for joining small parts that are difficult to weld.
The brazing material that joins the base materials melts and penetrates the fine details between the parts due to capillary action, making it possible to join complex shapes.
Nickel alloy brazing filler metals are mainly used for metal joining applications such as plate heat exchangers for high-efficiency water heaters, various industrial heat exchangers, EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) coolers, metallic catalytic substrates, etc.
Can be installed between joined parts with high precision, reducing assembly man-hours.
Reduces the amount of brazing filler metal used (compared to paste) and provides strong bonding with fewer voids. Moreover, reduces CO2 emissions by omitting the binder removal process, since it does not contain a binder and is environmentally friendly.
Product Catalog Download
Click here to download the product catalog
Contact
Soft Magnetic Materials and Components (for Waxwood)
Major Operation Bases
ABOUT US
Leading sustainability by high performance
768,6
billion
18,877