Amorphous alloy (Metglas™)
We will contribute to the achievement of the SDGs by manufacturing with our customers around the world with amorphous alloys we supply, from energy conservation and CO2 reduction to the creation of a recycling-oriented society through recycling of materials.
Product Catalog Download
Click here to download the product catalog
Contact
Soft Magnetic Materials and Components (for Amorphous Transformer)
In recent years, energy savings have been an urgent issue as a countermeasure against global warming. As energy efficiency standards in each country have become more strict, soft magnetic core materials with lower core loss have been required to comply with these standards.
Amorphous metal is an alloy with a non-crystalline structure produced by ultra-rapid quenching (about 1 million ℃ per second) of a molten alloy. Because amorphous metal has no anisotropic properties, “which originated from a crystalline structure and hence no crystalline grain boundaries to prevent motion of magnetic domain walls”, it shows excellent magnetic properties such as high permeability and low loss while having a high-saturation magnetic flux density.
Amorphous alloy, whose main ingredient is Fe (iron), compared to conventional materials such as silicon steel, have a small no-load loss (iron loss), 1/3 ~ 1/5 that of silicon steel.
Therefore, they make a major contribution to energy conservation.
Proterial provides amorphous metal ribbon and are also building the recycling system.
Link
Features
Fe-based amorphous alloys have lower iron loss compared to grain-oriented electrical steels because of low hysteresis loss due to non-crystalline structure and low eddy current loss due to thin ribbon thickness and high electrical resistivity.
Common Alloys
Crystalline alloys have periodic atomic structures.
-

Image chart of atomic arrangement
-
-
Domain wall motion is impeded by
structural defects such as grain
boundaries. -
Local grain size and direction can be
varied by post-fabrication
treatments.
-
Amorphous Alloys
Non-crystalline (amorphous) alloys have random atomic structures.
-

Image chart of atomic arrangement
-
-
Random network of atoms results in
lack of crystalline anisotropy. -

Excellent Soft Magnetic Properties.
-
Magnetic properties can be widely
changed by heat treatments.
-
Manufacturing method and recycling system
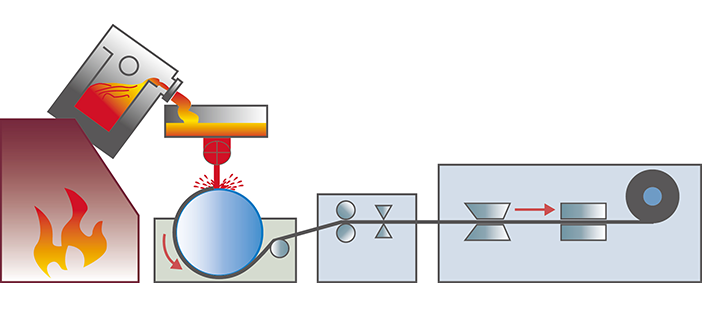
Production process of Amorphous Strip
Rapidly Quenched Casting Technology (Quenching Rate: ~106 ℃/s)
Fabricating Molten Alloy into Strip without Crystallization
Melting Furnace
Casting Roll
Casting Controller
Strip Winding
Application
Amorphous alloys are mainly used for pole transformers and industrial transformers, but due to their characteristics, they are also widely used in noise reduction parts, electronic circuit parts, EV parts, etc.
In recent years, it has been used for motor cores due to its low iron loss compared to electrical steel sheets.
Product Catalog Download
Click here to download the product catalog
Contact
Soft Magnetic Materials and Components (for Amorphous Transformer)
Electromagnetic Compatibility
EV related
Motor Core
Product Catalog Download
Click here to download the product catalog
Contact
Soft Magnetic Materials and Components (for Amorphous Transformer)
Major Operation Bases
ABOUT US
Leading sustainability by high performance
768,6
billion
18,877