GOS Ceramics Scintillator
It is mainly used in medical equipment such as X-ray CT(computed topology) analytical equipment. And also used in a checkpoint scanner, non-destructive testing equipment using radiation, radiation leakage testing equipment, etc for aviation and many industries, We have developed a high-density, high-performance GOS ceramic scintillator for CT technologies.
Product Catalog Download
Click here to download the product catalog
Contact
Inquiry to ceramic scintillator
Features of Proterial's GOS Ceramics Scintillator
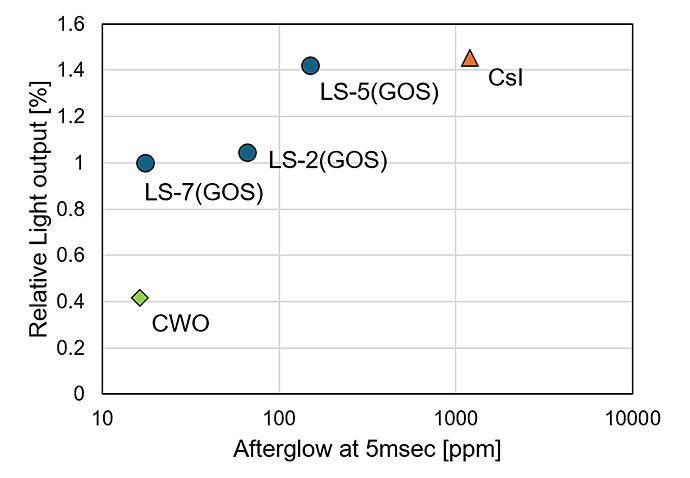
- 1Supersensitivity/Low afterglow/High Light Output
- 2Hight uniform sensitivity The central part of the wafer and the edges offer a uniform sensitivity.
- 3Maximized X-ray absorption coefficient The X-ray absorption coefficient is large, which enables the miniaturization of the scintillator.
- 4High X-Ray Stopping Power
- 5RoHS compliant
A Comparison between Proterial's GOS Ceramics Scintillators and Other Materials
| Material | PROTERIAL’S Materrials (GOS) | Other Materials | Remark | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS-5 | LS-7 | CsI:Tl+ | CWO | ||
| Light Output (% vs LS7) | 142 | 100 | 145 | 42 | Measurement value in our company |
| Afterglow (ppm) | 150 | 17 | 1,205 | 16 | @After 5ms |
| Decay time (ns) | ~ms | 3,000 | 680 | 5,000 | Literature value (ISBN 978-4-86476-245-8) |
| Density (g/cm3) | 7.3 | 7.3 | 4.5 | 7.9 | Literature value (ISBN 978-4-86476-245-8) |
| Peak Emission(nm) | 544 | 512 | 540 | 470 | Literature value (ISBN 978-4-86476-245-8) |
| X-ray Stopping (cm-1 at 100keV) | 19 | 19 | 9.2 | 22 | Calculation value in our company |
| Hygroscopicity | None | None | YES | None | Literature value (ISBN 978-4-86476-245-8) |
| RoHS/Reach Material | Compliance | Compliance | Compliance | Cd | RoHS 2018 |
Features of our scintillator array
- 1Contributing to larger detectors by increasing the size of the array
- 2Contributing to high-precision detectors through high-precision quality control of mechanical dimensions
- 3Realization of high-definition detectors by developing ultra-high-definition pixels
- 4Realization of ultra-narrow GAP array through high-precision machining process
Application
- 1X-ray Medical CTs
- 2Aviation cabin checkpoint baggage scanner
- 3Airport security system
- 4All radiation detection devices
- 5CT based system
- 6Passenger checkpoint screening
A scintillator is a material that absorbs radiation and converts it into visible or ultraviolet light. It is used to detect and measure radiation and is widely used in fields such as medical image diagnosis, radiation measurement, and baggage inspection equipment at airports.
Scintillators are used in the following applications:
- Medical imaging diagnostics:
- X-ray CT, PET scanners, etc.
- Radiation measurement:
- Radiation monitoring equipment and radiation measuring instruments.
- Particle physics:
- Detection of high-energy particles.
- Security:
- Baggage screening and personal screening equipment.
- Industrial X-ray CT:
- Non-destructive testing technology.
A scintillator is a material used to detect radiation and has the property of emitting light when exposed to radiation. There are many types of scintillator materials, but the following materials are currently commonly used in medical X-ray flat panels, medical CT equipment, and baggage inspection equipment for airports, etc.
- Medical X-ray flat panels:
- CsI、CWO(CdWO4)
- Medical CT equipment:
- GOS(Gd2O2S)、Garnet、CWO(CdWO4)
- Baggage inspection equipment for airports:
- GOS(Gd2O2S)、Garnet、Composite GOS、CWO(CdWO4)
Our company can mass produce GOS (Gd2O2S), Garnet, and Composite GOS for each of the above applications.
For details on the characteristics of our materials, please check the downloaded technical data.
The role of a scintillator in a detector is to detect radiation (e.g., X-rays, gamma rays, particle beams) and convert it into visible light or other measurable light signals.
The details are explained below.
- Radiation Absorption:
- A scintillator absorbs radiation and transfers its energy to the electrons inside. This process occurs when radiation is incident on the scintillator material.
- Conversion of Energy:
- The energy of the absorbed radiation brings the electrons in the scintillator into an excited state. Excited electrons emit photons (usually visible or ultraviolet light) as they return to their original energy level. This is called fluorescence.
- Light generation:
- The generated photons are emitted by the scintillator material and serve as a signal indicating the presence of radiation. This optical signal reflects the energy and position information of the radiation.
- Signal detection and amplification:
- The emitted photons are detected by a photodetector, such as a photodiode, and converted into an electrical signal. This electrical signal is further amplified and sent to electronic circuitry for analysis.
- Data analysis:
- The detected electrical signals are processed by an analyzer and converted into information such as radiation energy, location, and intensity. This information is used as data for medical images and radiation measurements.
The afterglow of a scintillator is a phenomenon in which a scintillator excited by radiation continues to emit light even after the radiation exposure has stopped. This characteristic is part of the time response characteristics of a scintillator, and specifically, it has the following characteristics:
- Afterglow Time:
- The duration of the afterglow varies depending on the scintillator material and can range from nanoseconds to milliseconds, or even seconds. The shorter the afterglow time, the faster the scintillator responds.
- Impact:
- Long afterglow can be problematic in applications (Example: medical CT scanners, etc.) that require fast and repeated detection, as it makes it difficult to separate successive radiation events. This is because the afterglow adds noise to the signal and reduces the time resolution.
- Application:
- Depending on the application of the scintillator, afterglow is an important selection criterion. For example, short afterglow times are preferred for medical imaging and high-speed radiation detection. On the other hand, there are applications where a long afterglow is not a problem or is even desirable. Afterglow characteristics are a key factor in the material selection and design of the scintillator. Signal processing techniques to compensate for the effects of afterglow are also important.
A scintillator array is a structure in which multiple scintillator elements are arranged in a lattice pattern. It is used for the purpose of wide-range radiation detection and high-resolution image acquisition. Scintillator arrays play a key role in medical image diagnosis and radiation measurement. The characteristics and roles of scintillator arrays are as follows.
- High-resolution image acquisition:
- Scintillator arrays are made up of many small scintillator elements, allowing for high-resolution images, which allows for the detection of finer structures.
- Improved position resolution:
- The array structure allows the incident position of radiation to be identified with high precision, improving the position resolution, which helps to obtain accurate position information.
- High sensitivity:
- Capable of detecting even weak radiation signals.
- Improved accuracy:
- The location of radiation incidence can be determined with high precision.
- Efficient data collection:
- Cover a wide area at once and collect a lot of data efficiently.
Scintillator arrays play a key role in various fields due to their high resolution and wide range of detection capabilities, especially in the medical field where they contribute greatly to improving the accuracy of patient diagnosis and treatment.
The maximum size of scintillator arrays that we can currently supply is approximately 80mm x 60mm.
This size is subject to change due to changes in equipment, etc.
The minimum pixel size of the scintillator arrays that we can currently supply is 0.5mm x 0.5mm.
This size is subject to change due to changes in equipment, etc.
Industrial X-ray CT is a non-destructive testing technology used in the industrial field. Like medical CT scans, X-rays are irradiated onto an object, and the transmitted data is analyzed by a computer to generate cross-sectional and 3D images. This allows detailed observation of the internal structure of an object.
Main Applications:
- Quality control:
- Used to detect internal defects in products (cracks, voids, foreign material inclusions, etc.).
- Materials Analysis:
- Analyze the internal structure of composites and metals to evaluate their properties and composition.
- Dimensional Measurement:
- Create precise 3D models and measure your product's dimensions precisely.
- Reverse Engineering:
- Creating detailed 3D models of existing parts or products to support innovative designs or improvements.
Advantage:
- Non-destructive testing:
- This allows for the internal inspection of an object without destroying it, so inspections can be conducted without compromising the reliability of the product.
- High accuracy:
- Even the smallest defects and structures can be detected with high accuracy.
- Fast:
- Test results are available in a short time, allowing for efficient quality control.
Yes, scintillators are also used in X-ray CT scanners for baggage inspection at airports, etc.
Scintillators play a key role in airport baggage inspection systems, contributing to improved.
security and efficient inspection processes.
Below, we explain the role and importance of scintillators in X-ray CT scanners used for airport baggage.
inspection.
- X-ray detection:
- X-ray CT scanners use the principle that X-rays are attenuated according to density differences inside the object as they pass through the baggage. A scintillator is used to convert the attenuated X-rays into visible light.
- High sensitivity:
- The high sensitivity of the scintillator means that even tiny amounts of X-rays can be efficiently converted into visible light, enabling the detection of minute structures.
- Rapid response:
- Scintillators respond quickly, producing images in real time, which is important for airport security screening to speed up screening without disrupting passenger flow.
- High-resolution images:
- The use of scintillators provides high-resolution images, allowing for detailed inspection of the interior of baggage, improving the accuracy of detecting dangerous goods.
- Practical use cases:
- Explosives detection:
High-resolution CT images are needed to detect explosives and weapons hidden in baggage.
Density difference analysis:
Distinguishing between varied materials such as food, liquids and electronic devices and analyzing the differences in their density to identify suspicious objects.
Consider the following points when selecting a scintillator material:
- Luminous Efficacy:
- Having high light output.
- Afterglow Time:
- The response speed is appropriate for the application.
- Durability:
- Able to withstand environmental conditions.
- Cost:
- It is economically feasible.
Product Catalog Download
Click here to download the product catalog
Contact
Inquiry to ceramic scintillator
Major Operation Bases
ABOUT US
Leading sustainability by high performance
768,6
billion
18,877